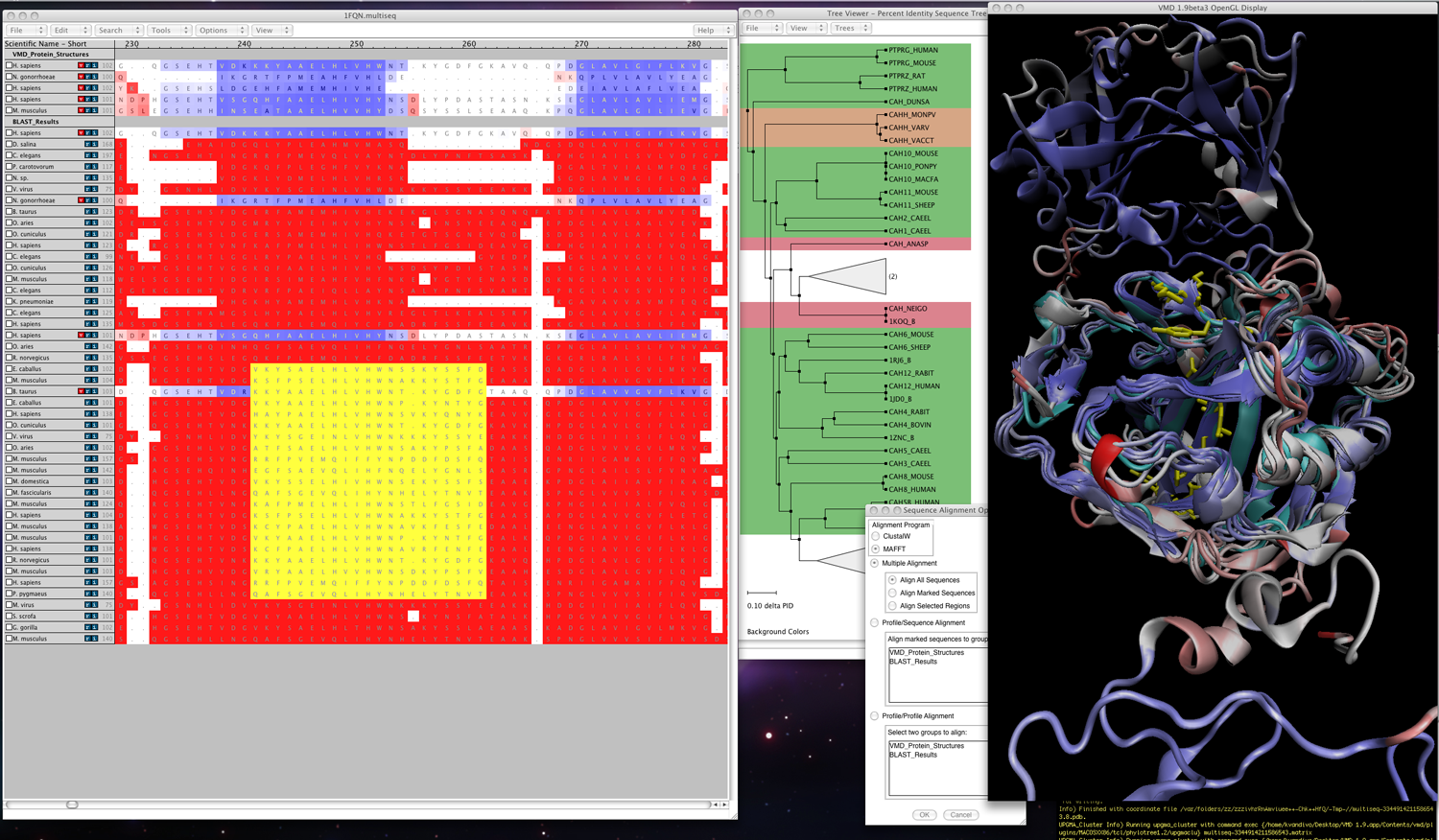
 |
MultiSeq (shown in Fig. 1) is a unified bioinformatics analysis environment that allows one to organize, display, and analyze both sequence and structure data for proteins and nucleic acids. MultiSeq was created to allow biomedical researchers to study the evolutionary changes in sequence and structure of proteins across all three domains of life, from bacteria to humans. The comparative sequence and structure metrics as well as analysis tools introduced in the
article by O'Donoghue and Luthey-Schulten 1are part of MultiSeq. In particular, the Luthey-Schulten group has included a structure-based measure of homologyFor publication of scientific results based completely or in part on the use of MultiSeq, please reference:
Elijah Roberts, John Eargle, Dan Wright, and Zaida Luthey-Schulten. ``MultiSeq: Unifying sequence and structure data for evolutionary analysis.'' BMC Bioinformatics, 2006, 7:382.