


Next: About this document ...
Up: Appendices
Previous: Appendix B:
Contents
Appendix B: 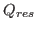 Structural Similarity per Residue
Structural Similarity per Residue
Here we define another metric, called Q , that is derived from Q which is used to measure the structural conservation of the environment of each
residue in the alignment. Q
, that is derived from Q which is used to measure the structural conservation of the environment of each
residue in the alignment. Q is a measure of the similarity of the
C
is a measure of the similarity of the
C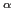 -C
-C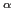 distances between a particular residue and all other aligned residues, excluding nearest neighbors, in a set of aligned proteins.
The result is a value between 0 and 1 that describes the similarity of the
structural environment of a residue in a
particular protein to the environment of that same residue in all other proteins in the set. Lower scores represent low similarity and higher scores high
similarity.
If the set of proteins represents an evolutionarily balanced set, then structural similarity corresponds to structural conservation. Formally,
Q
distances between a particular residue and all other aligned residues, excluding nearest neighbors, in a set of aligned proteins.
The result is a value between 0 and 1 that describes the similarity of the
structural environment of a residue in a
particular protein to the environment of that same residue in all other proteins in the set. Lower scores represent low similarity and higher scores high
similarity.
If the set of proteins represents an evolutionarily balanced set, then structural similarity corresponds to structural conservation. Formally,
Q is defined as follows:
is defined as follows:
![\begin{displaymath}
Q_{res}^{(i,n)} = \aleph \mathop{\sum _{(m\not=n)}^{proteins...
...ime }j^{\prime }}^{(m)} \right)^{2}}{2\sigma ^{2}_{ij}}\right]
\end{displaymath}](img48.png) |
(1) |
where
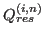 is the structural similarity of the
is the structural similarity of the 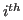 residue in the
residue in the 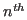 protein,
protein, 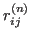 is the
is the 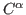 -
-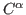 distance between residues
distance between residues 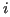 and
and 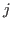 in protein
in protein 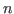 and
and
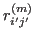 is the
is the 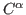 -
-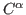 distance between the residues in
protein
distance between the residues in
protein 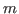 that correspond to residues
that correspond to residues 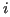 and
and 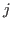 in protein
in protein 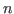 . The variance is related to the sequence separation between residues
. The variance is related to the sequence separation between residues 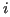 and
and 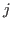 ,
,
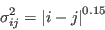 |
(2) |
and the normalization is given by
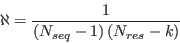 |
(3) |
where 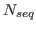 is the number of proteins in the set,
is the number of proteins in the set, 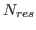 is the number of residues in protein
is the number of residues in protein 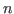 , and
, and 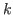 is 2 when residue
is 2 when residue 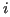 is the N- or
C-terminus otherwise 3.
is the N- or
C-terminus otherwise 3.
In order to know which residues correspond to each other across the set of proteins, Q requires a multiple sequence alignment (MSA) of the
proteins' sequences. Typically the MSA is generated using a structural alignment program.
requires a multiple sequence alignment (MSA) of the
proteins' sequences. Typically the MSA is generated using a structural alignment program.



Next: About this document ...
Up: Appendices
Previous: Appendix B:
Contents
multiseq@scs.uiuc.edu
![\begin{displaymath}
Q_{res}^{(i,n)} = \aleph \mathop{\sum _{(m\not=n)}^{proteins...
...ime }j^{\prime }}^{(m)} \right)^{2}}{2\sigma ^{2}_{ij}}\right]
\end{displaymath}](img48.png)
![]() is the structural similarity of the
is the structural similarity of the ![]() residue in the
residue in the ![]() protein,
protein, ![]() is the
is the ![]() -
-![]() distance between residues
distance between residues ![]() and
and ![]() in protein
in protein ![]() and
and
![]() is the
is the ![]() -
-![]() distance between the residues in
protein
distance between the residues in
protein ![]() that correspond to residues
that correspond to residues ![]() and
and ![]() in protein
in protein ![]() . The variance is related to the sequence separation between residues
. The variance is related to the sequence separation between residues ![]() and
and ![]() ,
,
![]() is the number of proteins in the set,
is the number of proteins in the set, ![]() is the number of residues in protein
is the number of residues in protein ![]() , and
, and ![]() is 2 when residue
is 2 when residue ![]() is the N- or
C-terminus otherwise 3.
is the N- or
C-terminus otherwise 3.
![]() requires a multiple sequence alignment (MSA) of the
proteins' sequences. Typically the MSA is generated using a structural alignment program.
requires a multiple sequence alignment (MSA) of the
proteins' sequences. Typically the MSA is generated using a structural alignment program.