


Next: Appendix B:
Up: Appendices
Previous: Appendices
Contents
In MultiSeq, Q has been generalized to measure the fraction of similar contact distances
between all the aligned residues in two homologous proteins or RNA molecules. This term computes the
fraction of  -
- (or
(or 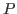 -
-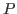 ) pair distances that are the
same or similar between two aligned structures. ``Evaluationg protein
structure-prediction schemes using energy landscape theory''
by Eastwood, M.P., C. Hardin, Z. Luthey-Schulten, and P.G. Wolynes in IBM J . Res. Dev. 45: 475-497. 2001.
) pair distances that are the
same or similar between two aligned structures. ``Evaluationg protein
structure-prediction schemes using energy landscape theory''
by Eastwood, M.P., C. Hardin, Z. Luthey-Schulten, and P.G. Wolynes in IBM J . Res. Dev. 45: 475-497. 2001.
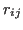 is the distance between a pair of
is the distance between a pair of  (or P) atoms.
(or P) atoms.
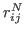 is the
is the  -
- distance between residues
distance between residues
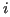 and
and 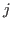 in the native state of a protein or RNA.
in the native state of a protein or RNA.
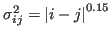 is the standard deviation, determining the width of the Gaussian function.
is the standard deviation, determining the width of the Gaussian function.
 is the number of residues of the protein being considered.
is the number of residues of the protein being considered.
multiseq@scs.uiuc.edu
![\begin{displaymath}
Q=\frac{2}{ (N-1)(N-2)} \sum _{i<j-1}\exp \left[ -\frac{\left( r_{ij}-r^{N}_{ij}
\right)^{2}}{2\sigma ^{2}_{ij}}\right]
\end{displaymath}](img10.png)
![]() is the distance between a pair of
is the distance between a pair of ![]() (or P) atoms.
(or P) atoms.
![]() is the
is the ![]() -
-![]() distance between residues
distance between residues
![]() and
and ![]() in the native state of a protein or RNA.
in the native state of a protein or RNA.
![]() is the standard deviation, determining the width of the Gaussian function.
is the standard deviation, determining the width of the Gaussian function.
![]() is the number of residues of the protein being considered.
is the number of residues of the protein being considered.